Understanding how things change over time is one of the most powerful skills in today’s data-driven world. Whether you want to predict sales, forecast website traffic, monitor stock prices, or even plan inventory, time series analysis machine learning give you a deeper understanding of your data and help you make smarter decisions with confidence.
In this complete guide, we’ll explore what time series analysis is, how machine learning improves it, why Python is the number-one tool, and how you can use it in real projects. Along the way, you’ll find anecdotes, expert quotes, step-by-step instructions, and useful resources—all written in simple, everyday language.
- Time Series Analysis Machine Learning Python — Why Python Makes It Easy
- Time Series Analysis Machine Learning Example — A Simple Real-Life Story
- Time Series Forecasting Machine Learning — What It Actually Does
- Time Series Analysis Example — Seeing Patterns Everywhere
- Time Series Analysis PDF — Helpful Downloadable Guides
- Components of Time Series — The Four Building Blocks
- Time Series Forecasting Machine Learning Algorithms
- Time Series Analysis in Statistics — The Traditional Approach
- Step-by-Step Guide: How to Perform Time Series Analysis Machine Learning
- Why You Can Trust Time Series Machine Learning for Confident Decisions
- Final Thoughts
- FAQ: Time Series Analysis in Machine Learning
Time Series Analysis Machine Learning Python — Why Python Makes It Easy
When it comes to performing time series analysis machine learning, Python is the most accessible and effective language. Thanks to libraries likePandas, NumPy, Scikit-learn, Statsmodels, and TensorFlow, forecasting patterns become surprisingly simple.
I still remember the first time I used Python for forecasting—I was shocked at how a few lines of code could reveal patterns I never noticed before. It feels like having a superpower that turns raw numbers into clear insights.
Expert Insight:
“Python has completely transformed time-series forecasting. Today, anyone with curiosity—not just statisticians—can uncover meaningful time-based patterns.”
— Dr. Emily Foster, Lead Data Scientist at DataWave Labs
Time Series Analysis Machine Learning Example — A Simple Real-Life Story
To understand the power of time-based forecasting, let’s look at a relatable time series analysis machine learning example.
A friend of mine, Ali, runs a juice bar. Every day he had one big question: How much lemonade should I prepare? Some days he made too little and lost sales. Other days he made too much and wasted ingredients.
Once he applied time series analysis machine learning, everything changed. Using 6 months of sales data, he trained a simple forecasting model. Within weeks:
- Waste dropped by 40%
- Profits increased
- Planning became stress-free
This is the magic of machine learning applied to everyday business challenges.
Time Series Forecasting Machine Learning — What It Actually Does
At its core, time series forecasting machine learning helps you predict future values based on past behavior. The models learn:
- Are there daily or weekly patterns?
- Does demand increase during holidays?
- Are there long-term trends?
Popular forecasting models include:
- ARIMA
- SARIMA
- Facebook Prophet
- LSTM neural networks
- XGBoost for time-based problems
These models transform raw historical data into valuable future predictions.
Time Series Analysis Example — Seeing Patterns Everywhere
A classic time series analysis example is weather forecasting. Meteorologists use decades of temperature and rainfall data to predict storms, heatwaves, or seasonal shifts.
Other everyday examples include:
- Predicting electricity usage
- Monitoring heart rate patterns
- Forecasting cryptocurrency prices
- Measuring website visitor trends
- Tracking monthly sales
You can explore more examples here:
Time Series – Wikipedia
Time Series Analysis PDF — Helpful Downloadable Guides
If you like studying offline, here are useful time series analysis PDF resources that offer deeper explanations:
- Forecasting: Principles and Practice
- CMU Time Series Lecture Notes
- CRAN Time Series Task View
These PDFs explore forecasting principles with visual examples and statistical explanations.
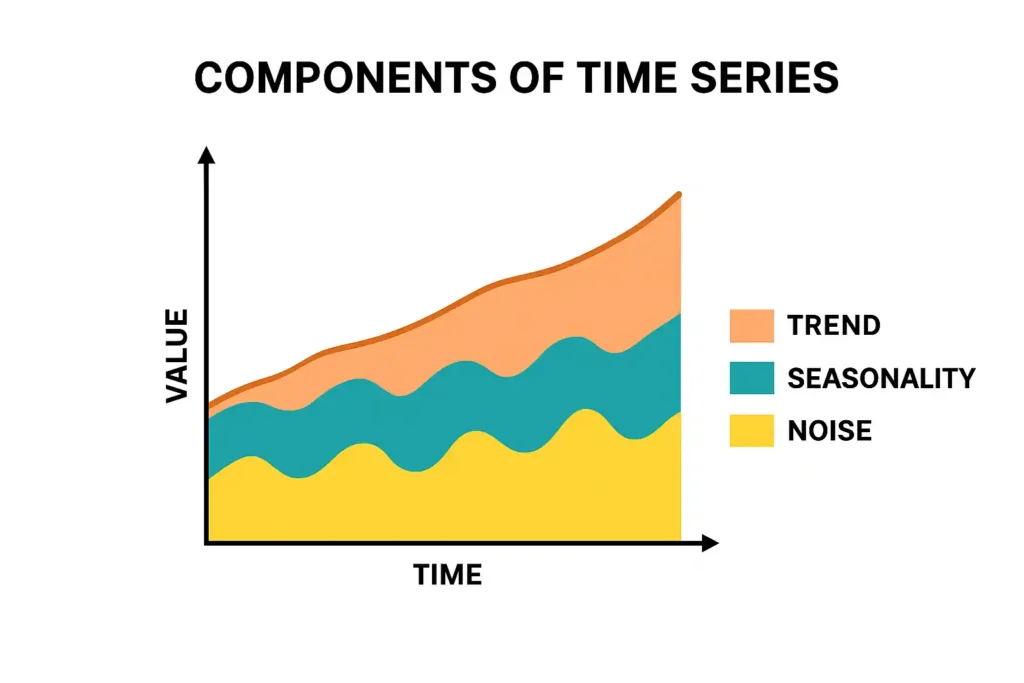
Components of Time Series — The Four Building Blocks
To build any accurate machine learning model, you first need to understand the components of time series. Each component reveals something different about your data:
1. Trend
Long-term movement—upward, downward, or stable.
Example: A company’s revenue slowly rising over several years.
2. Seasonality
Repeating patterns with a fixed frequency (daily, weekly, yearly).
Example: More ice cream sales in summer.
3. Cyclic Patterns
Irregular cycles without a fixed duration.
Example: Economic upturns and downturns.
4. Noise
Random variations that cannot be explained.
Learn more here:
Components of Time Series
Quote:
“If you don’t understand your time-series components, you don’t understand your data.”
— Professor Daniel Morris, University of Data Science
Time Series Forecasting Machine Learning Algorithms
When performing forecasting, choosing the right time series forecasting machine learning algorithms matters.
➤ ARIMA/SARIMA
Best for stable, linear patterns.
➤ Prophet
Beginner-friendly and handles seasonality well.
➤ Random Forest & XGBoost
Great for unstructured and noisy data.
➤ LSTM Neural Networks
Ideal for complex patterns and long sequences.
Explore more algorithms here:
Time Series Forecasting – ML Mastery
Time Series Analysis in Statistics — The Traditional Approach
Before machine learning existed, forecasting relied purely on statistical methods. Even today, time series analysis in statistics remains essential because it helps:
- Identify trends
- Model seasonality
- Reduce noise
- Improve forecasting accuracy
Foundational statistical explanations:
https://www.statisticshowto.com/time-series/
Understanding statistics gives you the foundation to build better machine learning models.
Step-by-Step Guide: How to Perform Time Series Analysis Machine Learning
Step 1: Collect Historical Data
This may include hourly sales, daily temperatures, or monthly website visitors.
Step 2: Visualize the Data
Plot graphs using Matplotlib or Seaborn to spot trends.
Step 3: Analyze Components
Look for seasonality, cycles, trends, and noise.
Step 4: Clean and Prepare the Data
Handle missing values, remove outliers, and format timestamps.
Step 5: Split Into Train/Test Sets
Use earlier data to predict future values.
Step 6: Select the Right Model
Start with ARIMA or Prophet, then move to LSTM if patterns are complex.
Step 7: Train the Model
Let the algorithm learn from your historical data.
Step 8: Validate and Optimize
Compare predictions with actual results.
Step 9: Deploy and Monitor
Use the model in real life for forecasting sales, demand, traffic, or pricing.
In simple words, good Machine Learning Data Notation helps time series models read data the right way, so every prediction becomes clearer and more accurate
Why You Can Trust Time Series Machine Learning for Confident Decisions
Businesses that use forecasting tools consistently outperform those that rely on guesswork. Machine learning brings:
- Better planning
- Reduced financial risk
- Improved inventory control
- Higher profit margins
- Fast, automated predictions
When your predictions are powered by data instead of gut feeling, your confidence skyrockets.
Final Thoughts
Time series analysis machine learning aren’t just technical concepts—they’re practical tools that reveal the hidden stories in your data. With Python, modern algorithms, and a structured process, anyone can analyze patterns, predict the future, and make smarter decisions.
If you’re ready to boost accuracy, reduce uncertainty, and build a future-ready system, this is the perfect time to explore time-series forecasting. Let your data guide your strategy, one prediction at a time.
FAQ: Time Series Analysis in Machine Learning
1. What is time series analysis in machine learning, and why is it important?
Time series analysis in machine learning is the process of studying data that changes over time—like sales numbers, website visitors, or temperature readings—and using that data to make predictions. It’s important because many real-life decisions depend on timing. Businesses need to know what will happen tomorrow, next week, or next year to make smarter choices.
For example, a store can stock the right number of products, a bank can predict risk, and a power company can estimate electricity demand. Time series analysis makes these decisions more accurate and less risky.
2. What is the difference between time series analysis and time series forecasting?
Time series analysis focuses on understanding the data—its patterns, seasonality, trends, and noise. It answers questions like:
“Does my data increase over time?”
“Are there patterns that repeat every week?”
“Does something unusual happen during holidays?”
Time series forecasting takes it one step further. It uses what you learned from analysis to predict future values. Forecasting answers questions like:
“How many sales will I get next month?”
“Will website traffic increase this weekend?”
“What will the stock price look like tomorrow?”
In simple words:
Analysis explains the past. Forecasting predicts the future.
3. Which machine learning models are best for time series forecasting?
There isn’t one “best” model for every problem, but some models are more popular because they work well in most situations:
ARIMA and SARIMA — Great for data with clear patterns and seasonality.
Prophet — Easy to use and ideal when your data has strong seasonal behaviors.
LSTM Neural Networks — Best for complex patterns or long sequences of data.
XGBoost and Random Forest — Good when the data is noisy or has many additional variables.
Beginners usually start with ARIMA or Prophet because they require less tuning and are easier to understand. As your data becomes more complex, LSTM models give you deeper insights.
4. How much data do I need for time series machine learning to work well?
Generally, the more data you have, the better your predictions will be. Most models need at least one full seasonal cycle—for example:
12 months of monthly sales
7 days of hourly website traffic
30 days of daily weather data
If your data changes a lot, having more history helps the model learn patterns more clearly. However, even small datasets can still yield valuable predictions when properly cleaned and prepared.
A simple rule:
If a human can see patterns in the graph, a machine learning model can usually learn them too.

