Pros and cons of big data is one of the most important questions in today’s world, whether you’re a business leader, student, or curious learner. Big data affects how decisions are made, how customers are understood, how products are developed, and how policies are shaped. It’s a powerful resource—but like any powerful tool, it comes with both advantages and challenges.
In this article, we’ll explore the benefits of big data and the disadvantages of big data, dive into lists like 10 advantages of big data and 10 disadvantages of big data, examine real-world applications of big data, and help you understand how to make confident decisions with data now and in the future.
- Benefits of Big Data: Why It’s Valuable
- Disadvantages of Big Data: What You Should Know
- 10 Advantages of Big Data You Should Know
- 10 Disadvantages of Big Data: Major Pitfalls
- Applications of Big Data Across Industries
- Pros and Cons of Big Data PDF: Resources for Further Study
- Pros and Cons of Big Data 2021 vs Today
- Final Thoughts: Is Big Data Worth It?
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) — Big Data Explained Clearly
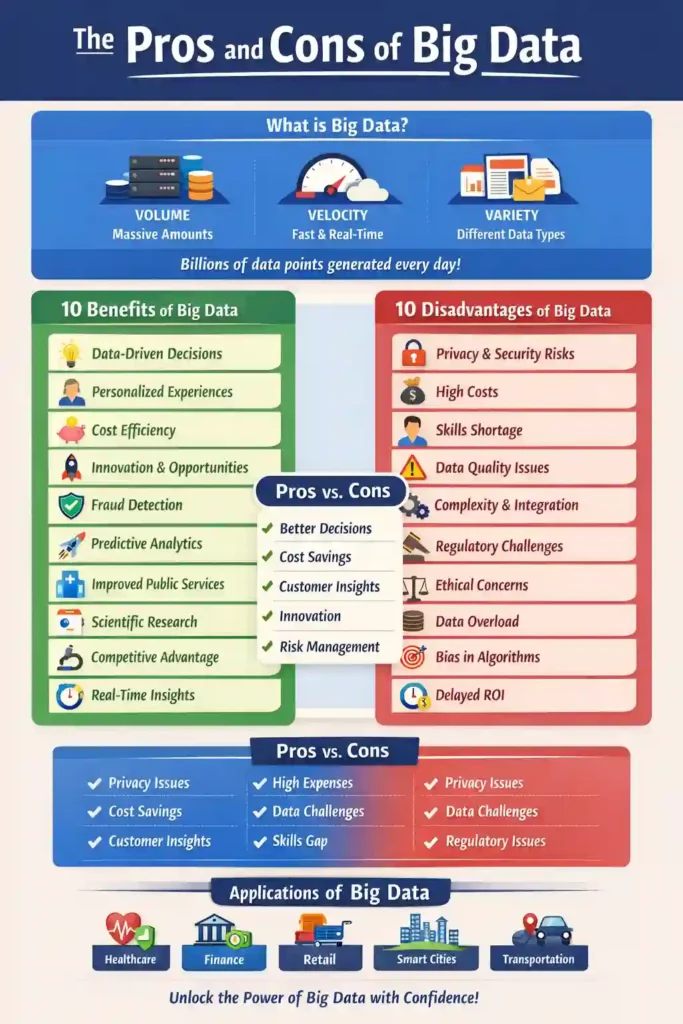
Benefits of Big Data: Why It’s Valuable
Despite the challenges, the benefits of big data make it an indispensable tool for organizations and society.
1. Data-Driven Decision Making
Big data analytics enables organizations to base decisions on evidence, not intuition. Analyzing patterns, trends, and historical data enables leaders to make more informed strategic choices. Analytics Vidhya
2. Enhanced Efficiency and Operational Improvements
Big data tools help companies identify inefficiencies in processes and resource allocation—leading to improved workflows, lower costs, and accelerated operations.
3. Personalized Customer Experiences
Through analytics, businesses can tailor products, content, and services based on individual preferences—boosting customer satisfaction and loyalty.
4. Competitive Advantage
Organizations that leverage big data insights effectively can innovate faster, anticipate market changes, and outperform competitors.
5. Improved Risk Management and Fraud Detection
Big data helps financial institutions and others detect anomalies, fraud patterns, and emerging risks—reducing losses and enhancing security. RF Wireless World
6. Innovation and New Opportunities
Analyzing customer behavior and market trends can reveal unmet needs, new services, and untapped revenue streams.
7. Predictive Analytics for Future Forecasts
Predictive modeling uses historical data to anticipate future trends—helping organizations prepare and strategize proactively.
8. Enhanced Public Services and Social Good
In sectors like healthcare, transportation, and urban planning, big data can optimize services, improve safety, and support evidence-based policy decisions. European Parliament
9. Scientific and Research Advancements
Researchers use big data to uncover insights in fields like biology, climate science, and epidemiology—advancing knowledge and breakthrough discoveries. arXiv
10. Real-Time Insights
Big data tools provide near-real-time analysis, which is essential for urgent decisions like supply chain disruptions or emergency response. Reddit
Disadvantages of Big Data: What You Should Know
While big data offers many benefits, it also comes with significant challenges. Understanding the disadvantages of big data can help you prepare and manage risks effectively.
1. Major Privacy and Security Risks
One of the most critical concerns with big data is data privacy and security. Collecting and analyzing large volumes of information often includes personal data, which can expose individuals and organizations to breaches, identity theft, and other cyber risks if not properly protected. Firms must invest in strong security and comply with privacy laws to prevent misuse.
2. High Implementation and Maintenance Costs
Setting up big data analytics infrastructure, tools, and storage solutions can be expensive. Costs include hardware, software, analytics platforms, cloud services, and expert professionals. For small and medium enterprises, these expenses pose real financial barriers. Konsyse
3. Complexity and Skills Gap
Working with big data isn’t simple. It requires specialized data scientists, analysts, engineers, and expertise in advanced technologies. Today’s demand for skilled professionals often outstrips supply, creating a gap that slows project adoption and increases costs. Towards AI
4. Data Quality and Reliability Issues
Not all data collected is useful. Poorly structured, inconsistent, or inaccurate data can lead to flawed analysis and unreliable outcomes. Ensuring high-quality data requires extra steps like cleaning, validation, and processing. RF Wireless World
5. Regulatory and Ethical Challenges
Big data projects must comply with laws like GDPR and other regional privacy frameworks. Ethical issues such as data bias, misuse, discrimination, and unauthorized surveillance also raise important questions about how data should be collected and used.
6. Data Overload and Management Difficulties
Big data can be overwhelming. The sheer volume and variety of information make storage, management, processing, and interpretation difficult without the right systems and workflows.
7. Integration Challenges
Merging large datasets from different sources and formats into existing systems can be technically complex and resource-intensive.
8. Bias and Discrimination in Algorithms
If data contains historical biases, the analytics models built on that data can accidentally perpetuate unfair or discriminatory outcomes, especially in sectors like hiring, lending, or law enforcement. Harvard Online
9. Ethical Concerns Around Data Use
Even with perfect compliance, how data is used raises important ethical questions. Personal data can be exploited for targeted advertising or political influence without user awareness or consent. European Parliament
10. Delayed Return on Investment
Unlike short-term projects, big data initiatives often take time before yielding measurable results. Planning and patience are essential.
The pros and cons of big data become easier to understand through analysis on big data, as it clearly shows where data adds value and where it needs careful handling.
10 Advantages of Big Data You Should Know
Here’s a clear list of 10 advantages of big data:
- Improved decision-making
- Enhanced operational efficiency
- Personalized customer interactions
- Stronger competitive positioning
- Fraud detection and enhanced risk management
- Innovation insights and new business opportunities
- Predictive analytics for foresight
- Cost optimization
- Better public service outcomes
- Real-time analytics for faster responses
10 Disadvantages of Big Data: Major Pitfalls
Here are the top 10 disadvantages of big data:
- Privacy and security concerns
- High implementation costs
- Skills shortages and expertise gap
- Data quality and reliability challenges
- Regulatory compliance complexity
- Ethical and bias issues
- Data overload and system overwhelm
- Integration challenges
- Delayed ROI
- Management complexity The Knowledge Academy
Applications of Big Data Across Industries
Applications of big data span nearly every industry:
- Healthcare: Predictive analytics for disease prevention and personalized treatment.
- Retail & E-commerce: Customer segmentation, inventory planning, and personalized offers.
- Finance: Fraud detection, risk modeling, and customer credit analysis. RF Wireless World
- Manufacturing: Supply chain optimization and production forecasting.
- Smart Cities: Traffic flow monitoring, public safety, and infrastructure management. European Parliament
- Telecommunications: Network optimization and churn prediction.
These real-world examples show how big data powers innovation, operational efficiency, and strategic growth.
Pros and Cons of Big Data PDF: Resources for Further Study
If you prefer downloadable resources, many reputable institutions and academic publications provide pros or cons big data PDF reports that explore trends, ethical frameworks, and case studies. Searching educational repositories or government websites can yield valuable materials for deeper reading.
Pros and Cons of Big Data 2021 vs Today
Conversations around the pros, cons of big data 2021 still influence how data is used today. While privacy, cost, and complexity were major topics then, advances in cloud computing, machine learning, and governance have made big data tools more accessible. Yet, challenges like ethical use and talent shortages remain relevant. Analytics Vidhya
Final Thoughts: Is Big Data Worth It?
Yes—when approached strategically.
The pros and cons of big data reveal a powerful resource that enables smarter decision-making, personalized experiences, operational efficiency, and innovation. At the same time, disadvantages of big data such as privacy risks, cost, and complexity require thoughtful planning, ethical governance, and strong security.
By understanding both sides and aligning your strategy with clear goals and responsible practices, you can confidently leverage big data for growth, insight, and innovation. Whether you’re exploring analytics for personal growth, business strategy, or organizational transformation, big data remains a defining force of the digital age.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) — Big Data Explained Clearly
1. What are the advantages and disadvantages of big data?
Advantages:
Big data lets organizations make smarter decisions based on patterns and trends found in huge datasets. It improves decision-making, helps companies understand customers better, and boosts operational efficiency. For example, a retailer analyzing big data might see exactly which products sell best in certain regions, helping them stock the right items at the right time. Big data also enables personalized experiences for users—like streaming platforms recommending shows based on your viewing history—and supports innovation and growth across industries like healthcare, finance, and public services. These insights lead to competitive advantage and better resource allocation.
Disadvantages:
However, big data comes with downsides. Privacy and security concerns are major issues because massive datasets often include sensitive personal information that must be protected from breaches. Setting up big data analytics systems can be costly, and there’s a strong demand for skilled professionals, which creates a talent gap. Poor data quality or bias can lead to incorrect conclusions, and legal or ethical challenges around data use and compliance add complexity.Konsyse+1
2. What is an advantage of big data?
One key advantage of big data is better, data-driven decision-making. By collecting and analyzing large amounts of information from many sources—such as customer interactions, sales records, or user behavior—organizations can uncover patterns and trends they couldn’t otherwise see. This allows leaders to make smarter choices that improve efficiency, reduce waste, and guide strategy with evidence rather than intuition. It’s especially useful in tailoring products and services to customer needs, which can increase satisfaction and boost competitive advantage.
3. What are the 5 P’s of big data?
The concept of the 5 P’s of big data isn’t as common as the “5 V’s,” but one practical way to think about the 5 P framework in the context of big data projects is as follows:
People – The skilled professionals (like data scientists and analysts) who make sense of data and interpret insights.
Purpose – A clear goal or reason for collecting and analyzing data (what problem you’re solving).
Process – The steps you take to collect, clean, transform, and analyze the data.
Platform – The tools and infrastructure used to process and store your data (cloud systems, analytics software, etc.).
Programmability – The use of programming skills (e.g., Python, R) to extract and manipulate data effectively.
This framework helps ensure that your big data initiatives are not just technical exercises, but strategic efforts aligned with real business or organizational goals.Easy Exam Notes
4. What are the pros and cons of data analysis?
Pros of data analysis:
Insight discovery: It reveals patterns and relationships in data that help you understand what’s happening and why.
Improved decisions: Using real data makes decisions more informed and less reliant on guesswork.
Efficiency and optimization: By analyzing operational or customer data, organizations can streamline processes and cut unnecessary costs.
Risk and trend prediction: Predictive analytics helps anticipate problems before they occur (like forecasting equipment failures).
Cons of data analysis:
Quality matters: If the data is messy, inaccurate, or incomplete, the results can be misleading.
Complex skills required: Effective analysis often needs trained analysts, statisticians, or data scientists.
Time and cost: Collecting and preparing data can be long and expensive, especially for large datasets.
Overreliance on data: Focusing only on data can overlook human judgment or contextual understanding, which also matters in decision-making.

