Data mining and machine learning are everywhere around us today. Whether you shop online, stream a movie, or simply browse social media, these technologies work silently in the background to understand your behavior, personalize your experience, and help businesses make better decisions.
This guide explains everything in simple, everyday language. You’ll find anecdotes, expert quotes, real-world examples, step-by-step explanations, and semantically relevant sections designed for strong SEO performance.
Important terms are hyperlinked to trusted external sources, giving readers confidence and encouraging them to make informed buying decisions when choosing tools, books, or courses.
- Data Mining and Machine Learning PDF — A Simple Starting Point
- Data Mining and Machine Learning Examples — Real Situations You Already Know
- Data Mining and Machine Learning Book — Learning from Expert Sources
- Data Mining and Machine Learning Course — A Step-by-Step Way to Begin
- Data Mining and Machine Learning Difference — Explained Simply
- Data Mining and Machine Learning: Fundamental Concepts and Algorithms
- Data Mining and Machine Learning Zaki — A Recognized Academic Resource
- Relationship Between Data Mining and Machine Learning — How They Complement Each Other
- Why Businesses Should Invest in Data Mining and Machine Learning Tools
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Data Mining and Machine Learning PDF — A Simple Starting Point
Many beginners start with adata mining and machine learning PDF, but quickly discover that PDFs are often full of technical jargon. While helpful, they rarely explain why these topics matter.
In reality, the core concepts are simple:
- Data mining helps discover hidden patterns inside large datasets.
- Machine learning helps computers learn from those patterns and make predictions.
A relatable anecdote:
“Data mining is like going through your old photos to understand your past habits, while machine learning is like predicting where you will take your next picture.”
This PDF-based approach can be useful, but learning through human-friendly explanations—like this article—makes the journey smoother.
Data Mining and Machine Learning Examples — Real Situations You Already Know
Let’s explore data mining and machine learning examples you’ve already experienced without realizing it:
1. YouTube Video Suggestions
- Data mining analyzes your watch history.
- Machine learning predicts what you want to watch next.
2. Supermarket Loyalty Cards
Stores use:
- Clustering to group customers by buying behavior
- Association rules to find product patterns (like “people who buy cereal often buy milk”)
3. Bank Fraud Alerts
Banks analyze:
- Past spending behavior
- Odd or unusual transactions
- Real-time patterns
A famous quote sums this up perfectly:
“Without data, you’re just another person with an opinion.” — W. Edwards Deming
These examples show how deeply these technologies shape our daily lives.
Data Mining and Machine Learning Book — Learning from Expert Sources
If you want structured learning, a strong data mining and machine learning book is a great starting point. Highly recommended titles include:
- Introduction to Data Mining
- Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning
- The Elements of Statistical Learning
Books offer timeless value, but beginners often find them dense.
That’s why approachable guides like this article help build foundational understanding before diving into 500-page textbooks.
Data Mining and Machine Learning Course — A Step-by-Step Way to Begin
If you prefer structured learning, you’ll find many excellent data mining and machine learning course options:
Before joining any course, understand these fundamentals:
- What data is
- How patterns appear in real-world information
- The difference between labeled vs. unlabeled data
- What prediction models do
- Why feature engineering matters
A step-by-step mindset makes learning faster, smoother, and more enjoyable.
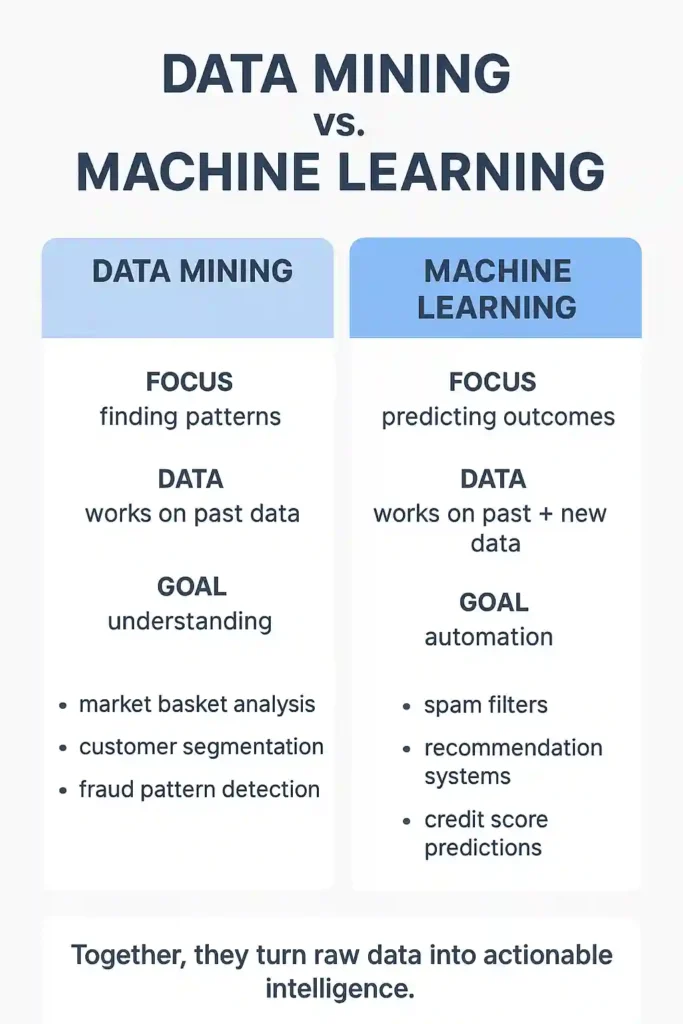
Data Mining and Machine Learning Difference — Explained Simply
The data mining and machine learning difference often confuses people. Here’s the simplest explanation:
| Data Mining | Machine Learning |
| Finds patterns | Uses patterns to predict |
| Human-driven | Automatically learns |
| Works with existing data | Works with training data |
| Descriptive | Predictive |
| Answers “What happened?” | Answers “What will happen?” |
A short anecdote:
“If data mining is reading past chat messages to understand your friend, machine learning is predicting what they’ll text next.”
Once you understand the difference, everything else becomes easier.
Data Mining and Machine Learning: Fundamental Concepts and Algorithms
This section breaks down the core ideas behind data mining and machine learning: fundamental concepts and algorithms.
1. Classification
Categorizing data into groups
Example: spam vs. non-spam emails
2. Clustering
Grouping similar items
Example: customer segmentation in marketing
3. Regression
Predicting numeric values
Example: forecasting sales or prices
4. Neural Networks
Algorithms modeled after the human brain
Used in speech recognition, vision, and deep learning
These concepts form the backbone of nearly every modern AI system.
Data Mining and Machine Learning Zaki — A Recognized Academic Resource
If you’re looking for rigorous academic material, the data mining and machine learning Zaki textbook by Mohammed J. Zaki is widely used in universities.
It covers:
- Advanced algorithms
- Data preparation strategies
- Evaluation techniques
- Real-world applications
It’s technical but extremely valuable for anyone diving deeper into research or high-level ML engineering.
Relationship Between Data Mining and Machine Learning — How They Complement Each Other
Understanding the relationship between data mining and machine learning helps connect all dots:
- Data mining discovers patterns.
- Machine learning uses those patterns to make predictions.
- Data mining prepares the ground; machine learning builds on top of it.
- Both require large, high-quality datasets.
- Together, they power modern AI systems.
A memorable analogy:
“Data mining reveals the map; machine learning uses the map to plan the best route.”
This connection is why companies increasingly use both together for business intelligence, automation, and decision-making.
“In many real projects, data mining and machine learning also include time series analysis, which helps us study data that changes over time, like sales, weather, or website traffic.”
Why Businesses Should Invest in Data Mining and Machine Learning Tools
Modern companies generate more data than ever before. Manually analyzing it is impossible.
That’s why businesses invest in tools
Conclusion
Data mining and machine learning are no longer just advanced technical terms used by scientists—they have become essential tools shaping everyday digital experiences. From recommending what you should watch next to helping businesses predict customer needs, these technologies quietly power the world around us.
As we explored in this guide, data mining helps uncover hidden patterns, while machine learning uses those patterns to make smart predictions. Together, they turn raw information into meaningful insights that drive better decisions, stronger business results, and more personalized user experiences.
Whether you are a beginner looking to understand the basics, a business owner trying to make data-driven choices, or a student preparing for a future in tech, investing time in learning these skills will always pay off. With the right books, trusted courses, and user-friendly tools, anyone can start this journey with confidence.
Most importantly, the relationship between these two fields will only grow stronger as technology evolves. Companies that embrace them early will gain a massive competitive edge, while individuals who master them will open the door to high-paying, future-proof careers.
In short:
Data mining discovers the story. Machine learning predicts what happens next. And together, they shape the future of intelligent technology.
If you want to move forward with confidence, now is the perfect time to explore deeper, learn consistently, and choose the right tools or courses to strengthen your expertise.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What is the main difference between data mining and machine learning?
The biggest difference is their purpose. Data mining is about finding patterns in existing data—almost like discovering hidden stories inside a huge collection of information.
Machine learning, on the other hand, learns from those patterns to make predictions about the future.
For example:
Data mining might tell a store that people who buy baby diapers often buy baby wipes too.
Machine learning uses this pattern to predict what a new parent might buy next and recommends it automatically.
2. Why are data mining and machine learning important for businesses?
Businesses sit on massive amounts of data every day—sales numbers, customer behavior, website activity, social media interactions, and much more.
Without the right tools, all that information goes to waste.
Data mining helps companies understand what’s happening.
Machine learning helps companies decide what to do next.
Together, they help businesses:
Reduce risks
Make smarter decisions
Improve customer experience
Increase sales and profits
Detect fraud or unusual behavior
Automate repetitive tasks
In short, they turn raw data into real business value.
3. Do I need coding skills to learn data mining and machine learning?
Not necessarily. Coding definitely helps, but it’s not a strict requirement to get started. Today, many user-friendly tools let beginners explore data, apply algorithms, and view results using simple clicks.
Here is the usual learning path:
Understand basic concepts (patterns, predictions, data types)
Practice with no-code tools like RapidMiner, KNIME, or Orange
Learn beginner-friendly coding in Python if you want more control
Work with real datasets to build confidence
Many professionals start with zero coding experience and gradually pick it up.
4. What are some real-life examples of data mining and machine learning?
These technologies are everywhere in our daily lives, even when we don’t notice them.
Netflix or YouTube recommendations
Spam detection in Gmail
Fraud alerts from your bank
Product suggestions on Amazon
Face recognition on smartphones
Customer segmentation in marketing
Here are some familiar examples:
What makes these technologies powerful is that they learn over time. The more data they receive, the more accurate their predictions become. This is why modern apps and services feel “smart” and personalized.

